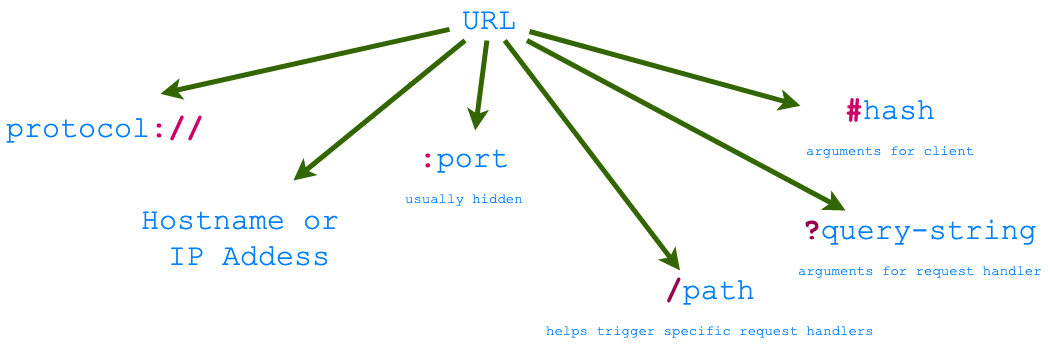
Uniform Resource Locator (URL)
The URL encodes request data that the client sends to a server. The client addresses the server and embeds all other parameters of the request in a URL. The Figures below shows an example of a URL, and components that make up a URL.
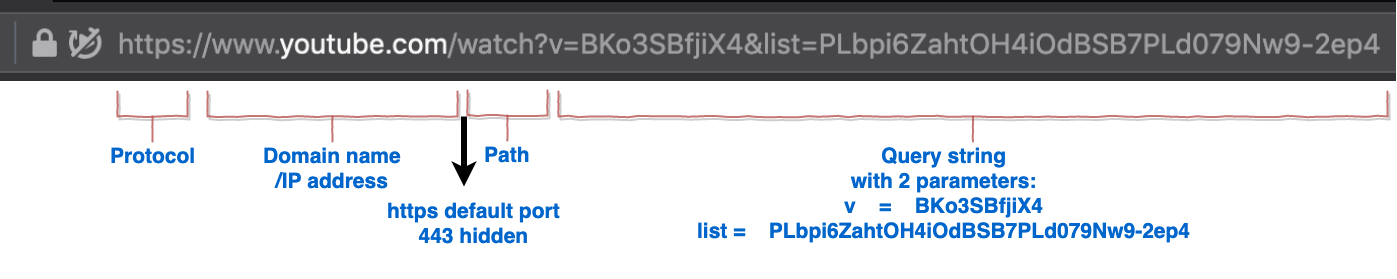
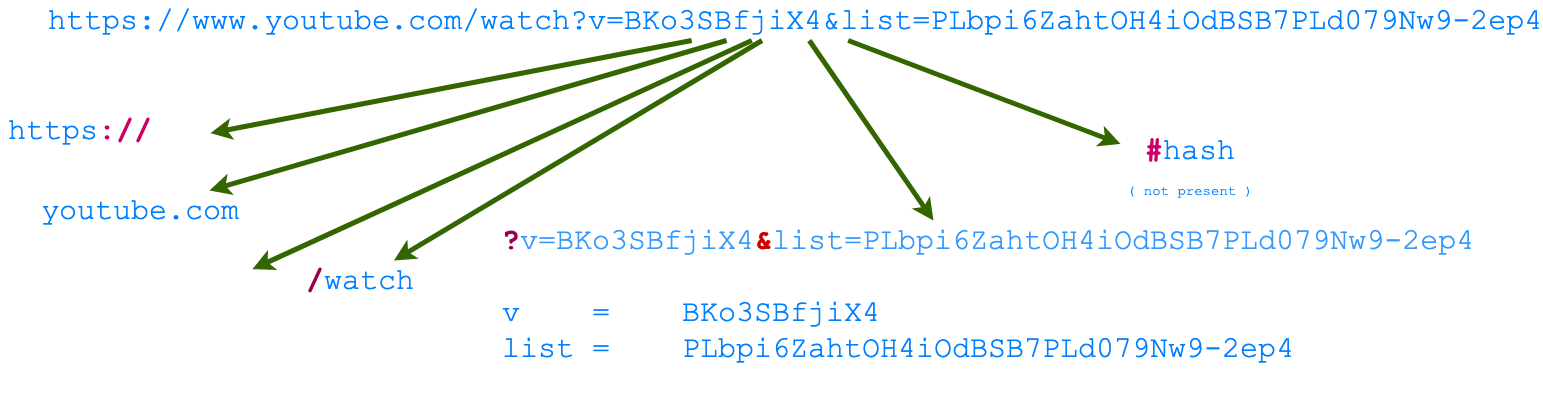
The URL provides the following basic information in order to route the request to the right server:
- Protocol scheme (
httporhttpsin case of websites/apps). - IP address (or DNS name which resolves to an IP address), which is unique to every computer including servers.
- Port. This allows request to be sent to different server programs on the same computer. Hidden in case of http/https and defaults to 80/443.
- Path, invoking the right request handler in the server.
- A query string that provides arguments to the request handler in key-value pairs.
Routing these request correctly is what
makes youtube.com respond with the video. Depending on the video ID
(argument v) a
different video is served. A playlist is displayed if a valid list
argument is present. Try opeing the following 2 urls:
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BKo3SBfjiX4&list=PLbpi6ZahtOH4iOdBSB7PLd079Nw9-2ep4
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BKo3SBfjiX4
Can you notice the difference?
The Figure below shows the parts of a generic URL.