Cascading Style Sheets (CSS)
CSS provides a way to style HTML tags. CSS was developed to make html 'clean'; that is to separate styles from tags. There are 3 important concepts in CSS:
- Properties
- Values
- Selectors
The easiest way to add CSS to an html tag is via the style attribute.
<TAG_NAME style='prop1:val1; prop2:val2; prop3:val3'>
content
</TAG_NAME>
CSS properties and values are written in pairs seperated by colon (:).
These pairs are themselves delimitted by semi-colons(;);
The attribute value of style is known as CSS declaration.
An external CSS file (.css extension file) consists on one or more
CSS Rules. A CSS rule is
made up of a CSS declaration and a CSS Selector.
CSS Rule:
<CSS Selector> {
<CSS Declaration>
}
We know what CSS declarations look like (value of a style
attribute). CSS selectors determine which tags the CSS declaration must
be applied to.
Box model
In order to fully understand CSS properties and values we first need to understand the CSS Box Model.
The Box Model specifies the parts of an HTML tag that can be 'styled':
- Content
- Padding
- Border
- Margin
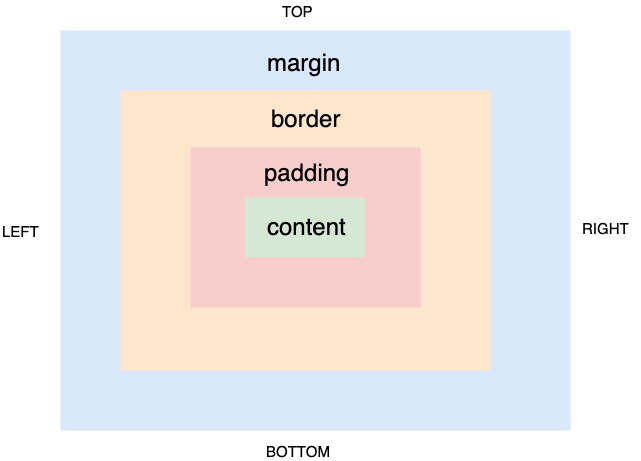
Each of these can be independently specified for each direction - top, right, bottom and left.
Value types
Distance
For any CSS property that needs to specify distance (e.g. border-width, height, witdth etc.) it is best to use the following units.
- px: Specifies distance in pixels
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
- %: Specifies distance as a percentage of the parent tag
width: 50%;
height: 50%;
(parent has width of 200px and height of 200px)
- vw/vh: Specifies distance as a percent of the viewpoet width/height
width: 30vw;
height: 20vh;
Color
Color values can be expressed in
-
Color name: Any valid CSS color name. Full list here.
-
Hexadecimal notation: e.g.:
#ffffff,#ff0000,#00ff00,#0000ffetc. -
RGB format: e.g.:
rgb(255,255,255),rgba(5,2,128,.3),rgb(25,155,35),rgb(5,25,255)etc. -
HSL format: e.g.:
hsl(120deg, 3%, 1%),hsl(10deg, 60%, 61%),hsl(40deg, 50%, 17%),hsl(0deg, 30%, 1%)etc.