Objects
Objects are a built in data type. An Object is a collection of properties(variables) and methods(functions), which are called members of the Object.
We have already looked at 2 built in
objects -- Strings and Arrays. They both have property length and many
different methods.
Object property and methods can be accessed via the dot (.) operator
or through box brackets ([]). For example the string property length
can be accessed as follows:
var s = "a test string";
var len = s.length; // using dot operator
var len = s["length"]; // using box brackets
Similarly any methods (say indexOf()) can be accessed similarly:
var s = "a test string";
var pos = s.indexOf(a); // using dot operator
var pos = s["indexOf"](a); // using box brackets
Object Syntax
var obj = { property_1: value_1, // property_# may be an identifier...
2: value_2, // or a number...
// ...,
'property n': value_n }; // or a string
Built In Objects
In this section we look at more built in objects.
The Object Object
There is a built-in Object called Object. This has one useful static
method that we will discuss here. Object.keys() returns the list of
all the objects member keys. It is very handy when you want to iterate
the Object.
var keys = Object.keys(location) // can be used to get keys on any object
for(var i = 0; i < keys.length; i++){
console.log("Key: " +keys[i]);
console.log("Key value: " + location[keys[i]]);
}
The Date Object
The Date object provides an easy way to store and manipulate dates in
JS.
Each Date object stores a particular date and time. Initializing a
Date object without arguments will give you the current date-time.
var now = new Date();
The new keyword
The new keyword is used to create a new object. Notice that we did not
use new() to create Arrays and Strings. That is because they are
built-in objects which can be instantiated without new(although you
could if you choose to).
As an object Date() has built in methods[Ref]:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
Date()
|
Gets today's date and time |
getDate()
|
Gets the day of the month for the specified date according to local time. |
getDay()
|
Gets the day of the week for the specified date according to local time. |
getFullYear()
|
Gets the year of the specified date according to local time. |
getHours()
|
Gets the hour in the specified date according to local time. |
getMilliseconds()
| Gets the milliseconds in the specified date according to local time. |
getMinutes()
| Gets the minutes in the specified date according to local time. |
getMonth()
| Gets the month in the specified date according to local time. |
getSeconds()
| Gets the seconds in the specified date according to local time. |
getTime()
| Gets the numeric value of the specified date as the number of milliseconds since January 1, 1970, 00:00:00 UTC. |
getTimezoneOffset()
| Gets the time-zone offset in minutes for the current locale. |
getUTCDate()
| Gets the day (date) of the month in the specified date according to universal time. |
getUTCDay()
| Gets the day of the week in the specified date according to universal time. |
getUTCFullYear()
| Gets the year in the specified date according to universal time. |
getUTCHours()
| Gets the hours in the specified date according to universal time. |
getUTCMilliseconds()
| Gets the milliseconds in the specified date according to universal time. |
getUTCMinutes()
| Gets the minutes in the specified date according to universal time. |
getUTCMonth()
| Gets the month in the specified date according to universal time. |
getUTCSeconds()
| Gets the seconds in the specified date according to universal time. |
getYear()
| Deprecated - Gets the year in the specified date according to local time. Use getFullYear instead. |
setDate()
| Sets the day of the month for a specified date according to local time. |
setFullYear()
| Sets the full year for a specified date according to local time. |
setHours()
| Sets the hours for a specified date according to local time. |
setMilliseconds()
| Sets the milliseconds for a specified date according to local time. |
setMinutes()
| Sets the minutes for a specified date according to local time. |
setMonth()
| Sets the month for a specified date according to local time. |
setSeconds()
| Sets the seconds for a specified date according to local time. |
setTime()
| Sets the Date object to the time represented by a number of milliseconds since January 1, 1970, 00:00:00 UTC. |
setUTCDate()
| Sets the day of the month for a specified date according to universal time. |
setUTCFullYear()
| Sets the full year for a specified date according to universal time. |
setUTCHours()
| Sets the hour for a specified date according to universal time. |
setUTCMilliseconds()
| Sets the milliseconds for a specified date according to universal time. |
setUTCMinutes()
| Sets the minutes for a specified date according to universal time. |
setUTCMonth()
| Sets the month for a specified date according to universal time. |
setUTCSeconds()
| Sets the seconds for a specified date according to universal time. |
setYear()
| Deprecated - Sets the year for a specified date according to local time. Use setFullYear instead. |
toDateString()
| Gets the "date" portion of the Date as a human-readable string. |
toGMTString()
| Deprecated - Converts a date to a string, using the Internet GMT conventions. Use toUTCString instead. |
toLocaleDateString()
| Gets the "date" portion of the Date as a string, using the current locale's conventions. |
toLocaleFormat()
| Converts a date to a string, using a format string. |
toLocaleString()
| Converts a date to a string, using the current locale's conventions. |
toLocaleTimeString()
| Gets the "time" portion of the Date as a string, using the current locale's conventions. |
toSource()
| Gets a string representing the source for an equivalent Date object; you can use this value to create a new object. |
toString()
| Gets a string representing the specified Date object. |
toTimeString()
| Gets the "time" portion of the Date as a human-readable string. |
toUTCString()
| Converts a date to a string, using the universal time convention. |
valueOf()
| Gets the primitive value of a Date object. |
In Addition there are 2 static Date() methods[Ref]:
window Object (browser only)
For browser based JS, the window is the topmost object. All other
objects and variables are derived from the window object.
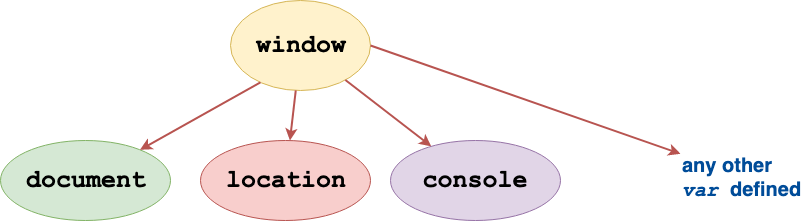
window ObjectTherefore when we write console.log() it is interpreted as
window.console.log().
The window object encapsulates other important objects such as --
location (which has useful members such as location.href,
location.hash, location.host, location.reload() etc.) and
document.
document Object (browser only)
Document Object Model (DOM)
The Document Object Model (DOM) is the represenation of the HTML document
within JS. The DOM has an object associated with each element (tag) within
the HTML document. The corresponding object can be used to read tag information (query
status of attributes and their values) as well as set
tag attribute values. Thus a DOM provides a way to read attribute values
from tags (including CSS declarations, since style is an attribute)
and set them.
The document Object has important DOM access methods such as
document.getElementById(), document.getElementsByTagName() ,
document.getElementsByClassName() etc
What about jQuery?
jQuery is a wrapper that implements different functions on top of JS.
The main dollar function ($()) in jQuery internally uses the DOM
(document Object, more specifically the document.querySelectorAll()
function).